Di Water Conductivity Units

In conclusion the proper conductivity range for di water is typically 5 10 6 s m.
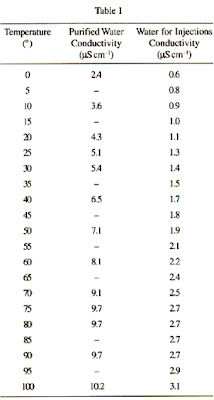
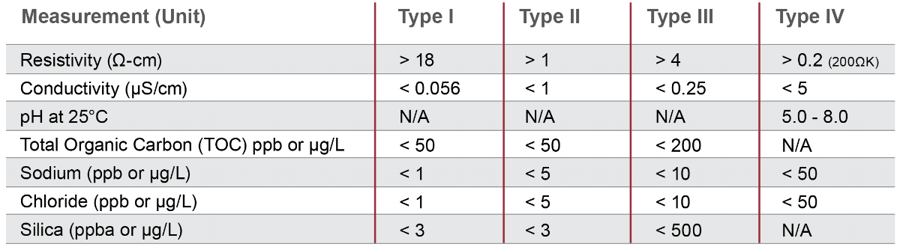
Di water conductivity units. Resistivity conductivity measurement of purified water. Deionized water di water diw or de ionized water often synonymous with demineralized water dm water is water that has had almost all of its mineral ions removed such as cations like sodium calcium iron and copper and anions such as chloride and sulfate deionization is a chemical process that uses specially manufactured ion exchange resins which exchange hydrogen and hydroxide ions. Thermal conductivity is a material property that describes ability to conduct heat. Most laboratory water purification systems contain a resistivity or conductivity meter and cell to monitor the purity level of the water.
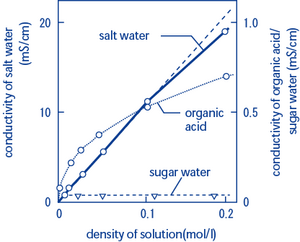
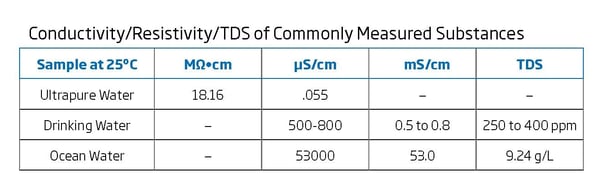
It is the amount of ionized substances or salts dissolved in the water which determines water s ability to conduct electricity. Resistivity is the reciprocal of conductivity and either may be used to inexpensively monitor the ionic purity of water. Pure water is not a good conductor of electricity. In many cases conductivity is linked directly to the total dissolved solids t d s.
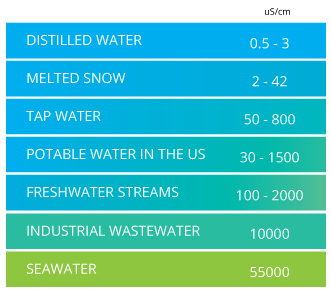
The de ionized water increases in quality with lower conductivities though higher grade de ionized di water will be more expensive and will take more time and energy to produce. Both cost and suitability are factors are important. High quality deionized water has a conductivity of about 0 5 μs cm at 25 c typical drinking water is in the range of 200 800 μs cm while sea water is about 50 ms cm or 50 000 μs cm. Thermal conductivity can be defined as the quantity of heat transmitted through a unit thickness of a material in a direction normal to a surface of unit area due to a unit temperature gradient under steady state conditions.
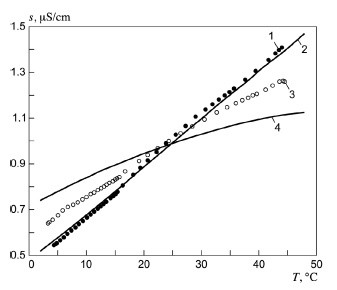
Ordinary distilled water in equilibrium with carbon dioxide of the air has a conductivity of about 10 x 10 6w 1 m 1 20 ds m. Conductivity is traditionally determined by connecting the electrolyte in a wheatstone bridge.